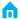
Jinghua horse stall with swing door stall simple safe strong door
Horses evolved to live on prairie grasslands and to cover long distances unfettered by artificial barriers. Therefore, when fenced in, accident potential must be considered. Horses will put their heads and legs through fences in an attempt to reach forage on the other side. They may run into fences if chased by another animal, or even when running at play if the fence (such as a wire fence) is not particularly visible. The smaller the area, the more visible and substantial a fence needs to be.
For exercise alone, a pen, run, corral or "dry lot" without forage can be much smaller than a pasture, and this is a common way that many horses are managed; kept in a barn with a turnout run, or in a dry lot with a shelter, feeding hay, allowing either no pasture access, or grazing for only a few hours per day. Outdoor turnout pens range greatly in size, but 12 feet (4 m) by 20 to 30 feet (9 m) is a bare minimum for a horse that does not get ridden daily. To gallop for short stretches, a horse needs a "run" of at least 50 to 100 feet (30 m). When kept in a dry lot, a barn or shelter is a must. If kept in a small pen, a horse needs to be worked regularly or turned out in a larger area for free exercise.
A sturdy and well-made wooden post and rail fence that is suitable for horses
Fences in pens must be sturdy. In close quarters, a horse may contact the fence frequently. Wire is very dangerous in any small pen. Pens are often made of metal pipe, or wood. Larger pens are sometimes enclosed in closely woven mesh, sometimes called "no climb" fencing. However, if a wire mesh is used in a small pen, the openings must be too small for a horse hoof to pass through.
The procuct advantage:
| 1.Fully hot dip galvanized finish or powder coated surface. |
| 2.A full range of design and style options. |
| 3.Swing window & swivel feeder are optional as accessories. |
| 4.Wood, wire mesh, round pipe are optional as infill material. |
| 5.Auto- lock and sliding systems give you a good experience |


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!